Recent Publications
Patrick Probst, Moritz Lindemann, Johanna R. Bruckner, Boshra Atwi, Dongren Wang, Felix R. Fischer, Marc Högler, Matthias Bauer, Niels Hansen, Michael Dyballa and Michael R. Buchmeiser*
The cationic molybdenum alkylidyne N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) complex [Mo(C-p-OMeC6H4)(OCMe(CF3)2)2 (IMes)][B(ArF4] (IMes = 1,3-dimesitylimidazol-2-ylidene) was selectively immobilized inside the pores of ordered mesoporous silica (OMS) with pore diameters of 66, 56, and 28 Å and used in the ring-expansion metathesis polymerization (REMP) of cyclic olefins to yield cyclic polymers. A strong confinement effect was observed for cis-cyclooctene (cCOE), 1,5-cyclooctadiene (COD), (+)-2,3-endo,exo-dicarbomethoxynorborn-5-ene ((+)-DCMNBE), and 2-methyl-2-phenylcycloprop-1-ene (MPCP), allowing for the synthesis of low-molecular-weight cyclic polymers even at a high monomer concentration. The exclusive formation of cyclic polymers was demonstrated by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry. Confinement also influences stereoselectivity, resulting in a pronounced increase in Z-selectivity and in an increased cis-syndiospecificity.
For further information please contact:
Prof. Michael R. Buchmeiser
Institute of Polymer Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
Kristof M. Altus, Yiping Shi, Patrick Probst, Jack H. Heaton, Matthew R. Gyton, Leonardo Lari, Michael R. Buchmeiser*, Philip W. Dyer*, Andrew S. Weller*
A tandem catalytic ensemble of solid-state molecular organometallic (SMOM) crystalline pre-catalysts are deployed under batch or flow conditions for the ethene to propene process (ETP). These catalysts operate at ambient temperature and low pressure, via sequential ethene dimerization, butenes isomerization and cross-metathesis. Under flow conditions the on-stream ethene conversion (55 %), initial propene selectivity (92 %), stability (71 % selectivity after 7 h) and low temperature/pressures are competitive with the best-in-class heterogeneous systems, marking a new, in crystallo, approach to ETP.
For further information please contact:
Prof. Michael R. Buchmeiser
Institute of Polymer Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
Koushani Kundu, Severin Haid, Moritz R. Schäfer, Wolfgang Frey, Johannes Kästner* and Michael R. Buchmeiser*
Stereoselective ring opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) of enantiomerically pure 2,3-dicarbomethoxynorborn-5-ene ((+)-DCMNBE) was accomplished by the action of cationic tetra- and pentacoordinated molybdenum imido alkylidene cyclic alkyl amino carbene (CAAC) complexes that are chiral at molybdenum. The same catalysts were also utilized to perform the ROMP of 2,3-dimethoxymethylnorborn-5-ene ((+)-DMMNBE). All complexes were moderately to highly active and showed high trans-isoselectivity, offering up to 97% trans-isotactic (it) repeat units. In all cases, tetracoordinated complexes were the active species, resulting in pentacoordinated transition states. A theoretical model was elaborated using the buried volume (% Vbur) values of all ligands from single-crystal X-ray analysis together with the structures of the density functional theory (DFT) generated molybdacyclobutane intermediates. The model demonstrates the steric effects of all ligands at molybdenum on the trans-isoselectivity of the reaction, as predicted by the turnstile mechanism, and includes a positive correlation between the bulky CAAC ligand with high values of % Vbur of the other ligands and a high trans-isoselectivity. It was also successfully extended to molybdenum imido alkylidene N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) complexes, proved to be of sufficient accuracy with a root mean squared error (RMSE) of 6.19% and was verified by Monte Carlo cross-validation (MCCV).
For further information please contact:
Prof. Michael R. Buchmeiser
Institute of Polymer Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
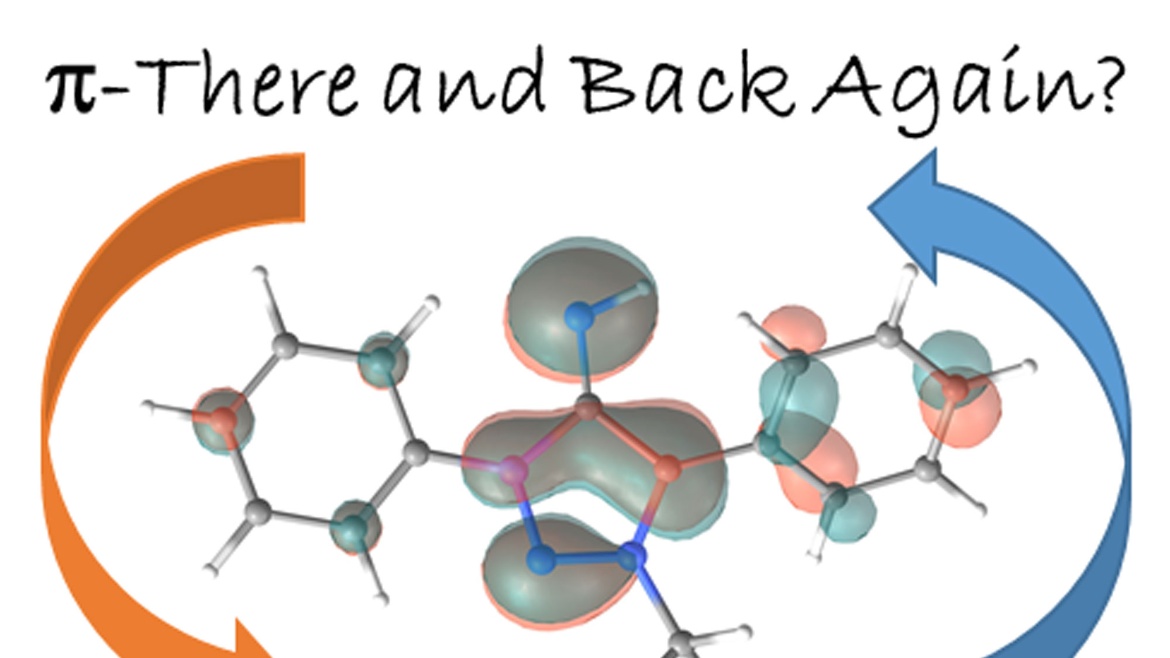
Nicholas Birchall, Fridolin Hennhöfer, Martin Nieger, Dietrich Gudat
A chromium complex carrying two benzanellated N-heterocyclic phosphenium (bzNHP) ligands was prepared by a salt metathesis approach. Spectroscopic studies suggest that the anellation enhances the π-acceptor ability of the NHP-units, which is confirmed by the facile electrochemical reduction of the complex to a spectroscopically characterized radical anion. Co-photolysis with H2 allowed extensive conversion into a σ-H2-complex, which shows a diverse reactivity towards donors and isomerizes under H−H bond fission and shift of a hydride to a P-ligand. The product carrying phosphenium, phosphine and hydride ligands was also synthesized independently and reacts reversibly with CO and MeCN to yield bis-phosphine complexes under concomitant Cr-to-P-shift of a hydride. In contrast, CO2 was not only bound but reduced to give an isolable formato complex, which reacted with ammonia borane under partial recovery of the metal hydride and production of formate. Further elaboration of the reactions of the chromium complexes with CO2 and NH3BH3 allowed to demonstrate the feasibility of a Cr-catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol. The various complexes described were characterized spectroscopically and in several cases by XRD studies. Further insights in reactivity patterns were provided through (spectro)electrochemical studies and DFT calculations.
Chem. Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202401714
For further information please contact:
Prof. Dietrich Gudat
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
Andreas Schneider, Thomas B.. Lystbænk, Daniel Markthaler, Niels Hansen and Bernhard Hauer
Terpene synthesis is at the heart of organic synthesis and often represents the state-of-the-art in synthetic methodologies. A remaining challenge is the correct three-dimensional assembly of the terpene skeleton via cationic cyclization of abundant linear precursors. Nature has been using this strategy for eons by employing the catalytic excellence of terpene cyclases. In this paper, we harness the synthetic power of engineered squalene-hopene cyclases and demonstrate the chemoenzymatic synthesis of ten chiral (mero-)terpenes with up to five stereocenters and >99% ee and de.
Nature communications, 2024, doi 10.1038/s41467/-024-448993
For further information please contact:
Prof. Bernhard Hauer
Institute of Biochemistry and Technical Biochemistry,
University of Stuttgart
Yannick Stöckl*, Katrin Gugeler, Celine M. Holzwarth, Wolfgang Frey, Sascha Wegner, Birgit Claasen, Anna Zens, Dietrich Gudat, Christian P. Sindlinger, Johannes Kästner*, and Sabine Laschat
Organometallics 2024, 43, 3, 330–340.
Enantioenriched boron chelates show promising synthetic and luminescent properties; however, the challenging synthesis makes these compounds scarce. In our earlier work, we established a chirality transfer from boron O,N-chelates toward enantioenriched C,N-chelates. This methodology proved to be quite robust, in terms of yields and selectivity. However, unexpected steric effects on stereocontrol prompted a deeper investigation of the chirality transfer. In order to gain a holistic understanding of this process, we studied the structure of the O,N- and C,N-chelates as well as the stability of the dative B–N bonds. Furthermore, the proposed ate-complex as a reaction intermediate could be characterized using heteronuclear (2D) NMR spectroscopy. For this ate-complex, a tridentate O,N,N-chelate effect of the borate anion with the Li-cation was observed. Additional experiments indicated that the borate formation governs the stereoselectivity of chirality transfer. For a successful chirality transfer, an unprecedented SN2-type breaking of the dative B–N bond with an organometallic nucleophile was identified by DFT calculations as the most likely reaction path. For other cases, decreased or inverse enantioselectivity was rationalized by a solvent-assisted pathway.
For further information, please contact:
Prof. Sabine Laschat
Institute of Organic Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
Jan S. Florenski, Noah Schellander, Prof. Dr.-Ing. Elias Klemm
Quantifying the active surface area of Mars-van-Krevelen catalysts is paramount for the elucidation of structure-property relationships and the knowledge-based catalyst development. Different cerium oxides were prepared via precipitation-based techniques. By altering conditions during precipitation, materials with a wide span of material properties were prepared. The influence of temperature during ammonia-based precipitation was investigated. When using Ce(IV) precursors an increase in precipitation temperature decreases the crystallite size while increasing specific surface area, attributed to an increase in nucleation rate. Sintering stability is also increased for materials precipitated at higher temperature. Measuring the total oxygen storage capacity (TOSC) values of the prepared materials showed that the TOSC is not strictly a function of BET surface area. Our results suggest that crystallites with a domain size under a certain threshold are not reduced via oxygen release but rather hydroxyl formation. A method was proposed with which the redox active surface area for polycrystalline ceria can be estimated on basis of the domain size obtained from Rietveld refinement. These findings were corroborated by CO oxidation light-off experiments in which the light-off temperature was found to correlate with the surface that can release oxygen reversibly, the Mars-van-Krevelen active surface area, rather than BET surface area.
ChemCatChem 2024, e202301
For further information, please contact:
Prof. Elias Klemm
Institute for Technical Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
Julian Ludwig, Christian Curado-Carballada, Stephan C. Hammer, Andreas Schneider, Svenja Diether, Nico Kress, Sergi Ruiz-Barragán, Sílvia Osuna* and Bernhard Hauer*
The interconversion of monoterpenes is facilitated by a complex network of carbocation rearrangement pathways. Controlling these isomerization pathways is challenging when using common Brønsted and Lewis acid catalysts, which often produce product mixtures that are difficult to separate. In contrast, natural monoterpene cyclases exhibit high control over the carbocation rearrangement reactions but are reliant on phosphorylated substrates. In this study, we present engineered squalene-hopene cyclases from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius (AacSHC) that catalyze the challenging isomerization of monoterpenes with unprecedented precision. Starting from a promiscuous isomerization of (+)-β-pinene, we first demonstrate noticeable shifts in the product distribution solely by introducing single point mutations. Furthermore, we showcase the tuneable cation steering by enhancing (+)-borneol selectivity from 1 % to >90 % (>99 % de) aided by iterative saturation mutagenesis. Our combined experimental and computational data suggest that the reorganization of key aromatic residues leads to the restructuring of the water network that facilitates the selective termination of the secondary isobornyl cation. This work expands our mechanistic understanding of carbocation rearrangements and sets the stage for target-oriented skeletal reorganization of broadly abundant terpenes.
For further information, please contact:
Prof. Bernhard Hauer
Institute of Biochemistry and Technical Biochemistry,
University of Stuttgart
New hydrazinium hydro-closo-borates with [BnHn]2– anions (n = 10 and 12) were obtained by direct reaction of the free acids (H3O)2[BnHn] with hydrazinium hydrate (N2H4 · x H2O) in aqueous solution. The three new compounds (N2H5)2[B10H10], (N2H5)2[B10H10] · 2 N2H4 and (N2H5)2[B12H12] · 2 N2H4 crystallize in the space groups P21/c, C2/c and P respectively. They contain up to 11 wt-% hydrogen. Two main kinds of bonding were observed in all crystal structures, classical hydrogen bonds (Nδ––Hδ+⋯Nδ–) and dihydrogen bonding between the negatively polarized hydrogen of the boron clusters and positively polarized hydrogen in hydrazinium cations (Bδ+–Hδ–⋯Hδ+–Nδ–). Thermal decomposition analyses of these compounds show that they absorb energy first, and then release a huge amount of energy upon decomposition and collapse of the structure. Due to the differently polarized hydrogen atoms in these compounds, hydrogen molecules (H2) are generated during the decomposition, which can be used as hydrogen fuel.
The most recent report on this can be found in L. W. Zimmermann, R. Aghaei Hakkak, M. Ranjbar, Th. Schleid: "Crystal Structures and Thermal Analyses of Three New High-Energy Hydrazinium Hydro-closo-Borates", Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 49, 1469–1477.
For further information please contact:
Prof. Thomas Schleid
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
Older publications
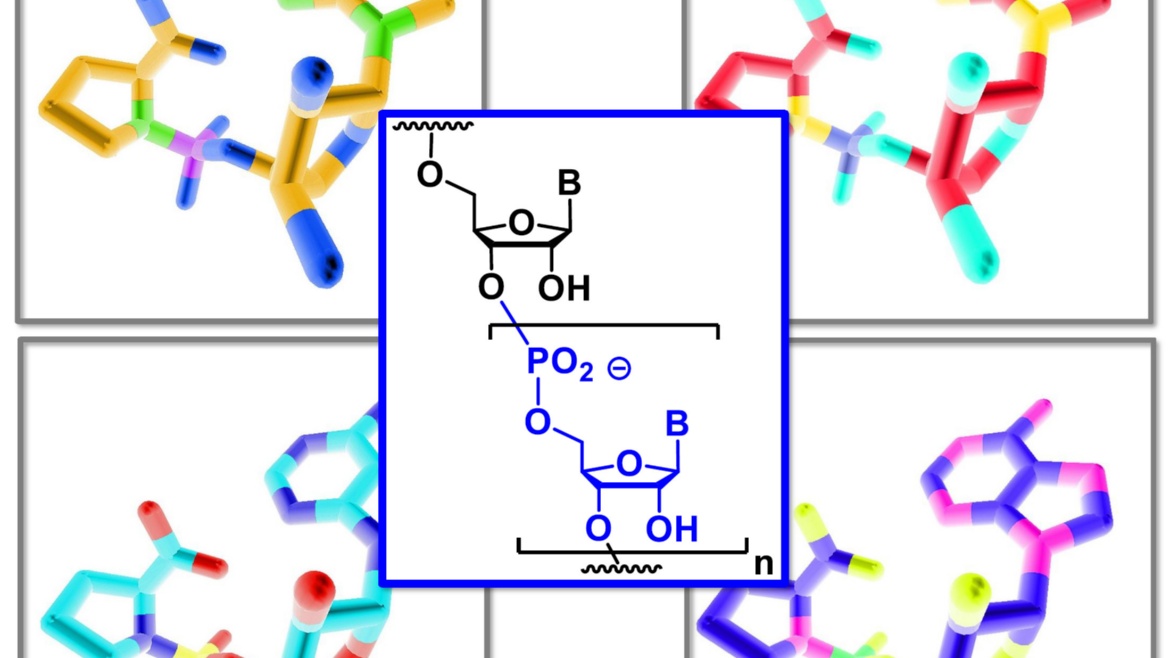
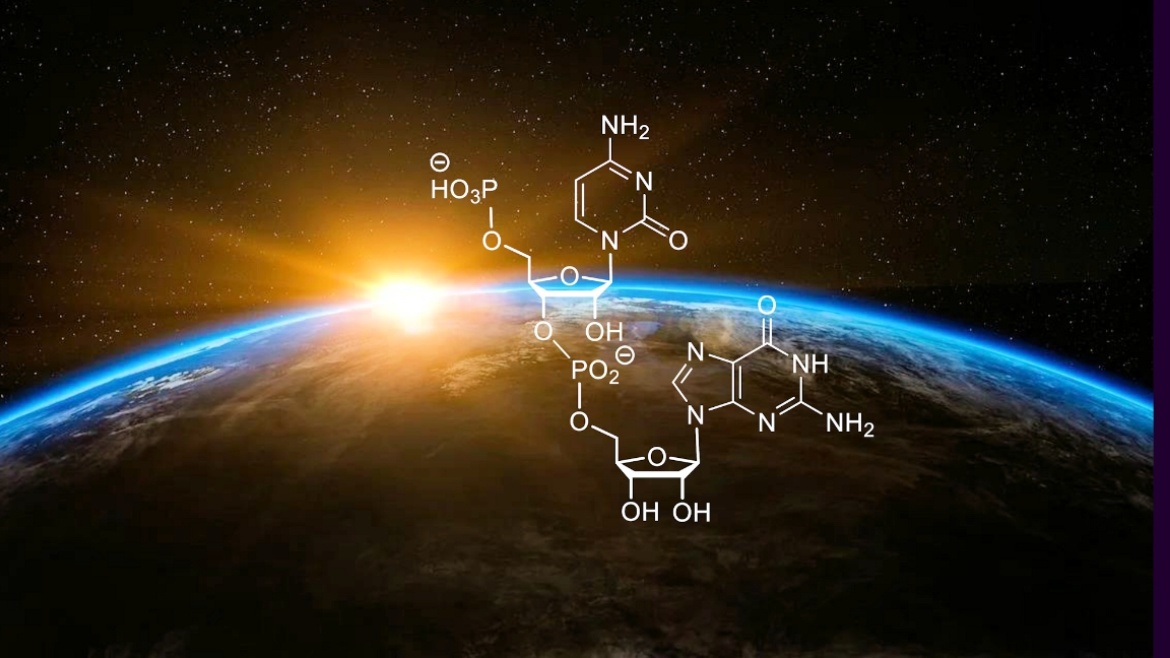
A publication by Prof. Clemens Richert's working group has appeared in the journal Angewandte Chemie. As part of a project in the Transregional Collaborative Research Center 235, it was demonstrated that the amino acid proline and individual building blocks of RNA react to form compounds that act as starting material for the enzyme-free genetic copying of RNA sequences. This previously unknown synergy between the building blocks of proteins and genetic material helps to explain the molecular origin of life.
Read the announcement here on the homepage of the Institute
or on the homepage of the SFB 235
For further information please contact:
Prof. Clemens Richert
Institute of Organic Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
S. Gergel, J. Soler, A. Klein, K. H. Schülke, B. Hauer, M. Garcia-Borràs und S. Hammer.
The direct regioselective oxidation of internal alkenes to ketones poses an important synthetic challenge. Now, directed evolution of a cytochrome P450 enzyme affords a ketone synthase that can efficiently oxidize internal arylalkenes directly to ketones with high chemo- and regioselectivity.
Nature Catalysis 2023
For further information please contact:
Prof. Bernhard Hauer
Institute of Biochemistry and Technical Biochemistry,
University of Stuttgart
Benjamin Aberle, Daniel Kowalczyk, Simon Massini, Alexander-N. Egler-Kemmerer, Sebastian Gergel, Stephan Hammer, Bernhard Hauer
Terpenes are natural compounds with diverse applications, but the available carbon scaffolds are limited by their biosynthesis from five carbon precursors. To gain access to non-natural terpenoids, we identified and engineered methyltransferases for late-stage C-methylation of unactivated alkenes. The engineering resulted in a 55-fold improvement of conversion of (E,E)-farnesol with > 99% selectivity. In total, five non-natural terpenoids were produced and isolated using this biocatalytic method. This opens new avenues for the modification of the carbon scaffold of terpenes.
For further information please contact:
Prof. Bernhard Hauer
Institute of Biochemistry and Technical Biochemistry,
University of Stuttgart
Andreas Schneider; Christian Curado; Thomas B. Lystbaek; Sílvia Osuna; Bernhard Hauer
Angewandte Chemie: DOI number 10.1002/anie.202301607
The synthetic power of terpene cyclases is of broad academic as well as industrial interest as it can cut down synthetic routes to complex cyclic terpenes to essentially one step. However, these enzymes usually lack catalytic turnovers and stability under the new-to-nature conditions. Teaming up with the BioCompLab, Girona of Silvia Osuna, we showcase the synergy of tailoring the active site and entrance tunnel of the squalene-hopene cyclase for the stereocontrolled cationic cyclization of E,E-homofarnesol to (–)-ambroxide with >100.000 total turnovers.
For further information please contact:
Prof. Bernhard Hauer
Institute of Biochemistry and Technical Biochemistry,
University of Stuttgart
Dongyang Chen, Francisco Tenopala-Carmona, Julius A. Knöller, Andreas Mischok, David Hall, Subeesh Madayanad Suresh, Tomas Matulaitis, Yoann Olivier, Pierre Nacke, Frank Gießelmann, Sabine Laschat, Malte C. Gather, Eli Zysman-Colman
The use of thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) emitters and emitters that show preferential horizontal orientation of their transition dipole moment (TDM) are two emerging strategies to enhance the efficiency of OLEDs. We present the first example of a liquid crystalline multi-resonance TADF (MR-TADF) emitter, DiKTa-LC. The compound possesses a nematic liquid crystalline phase between 80 °C and 110 °C. Importantly, the TDM of the spin-coated film shows preferential horizontal orientation, with an anisotropy factor, a, of 0.28, which is preserved in doped poly(vinylcarbazole) films. Green-emitting (λEL = 492 nm) solution-processed OLEDs based on DiKTa-LC showed an EQEmax of 13.6%. We thus demonstrate for the first time how self-assembly of a liquid crystalline TADF emitter can lead to the so-far elusive control of the orientation of the transition dipole in solution-processed films, which will be of relevance for high-performance solution-processed OLEDs.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, e202218911.
For further information please contact:
Prof. Sabine Laschat
Institute of Organic Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
Shubhadeep Chandra, Dr. Arijit Singha Hazari, Dr. Qian Song, David Hunger, Dr. Nicolás. I. Neuman, Prof. Dr. Joris van Slageren, Prof. Dr. Elias Klemm, Prof. Dr. Biprajit Sarkar.
For further information please contact:
Prof. Biprajit Sarkar
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
Simon Suhr, Robert Walter, Julia Beerhues, Uta Albold und Biprajit Sarkar
For further information please contact:
Prof. Biprajit Sarkar
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
Richard Rudolf, Nicolás I. Neuman, Robert R. M. Walter, Mark R. Ringenberg und Biprajit Sarkar
Angew. Chemie 2022, 61, e202200653
For further information please contact:
Prof. Biprajit Sarkar
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
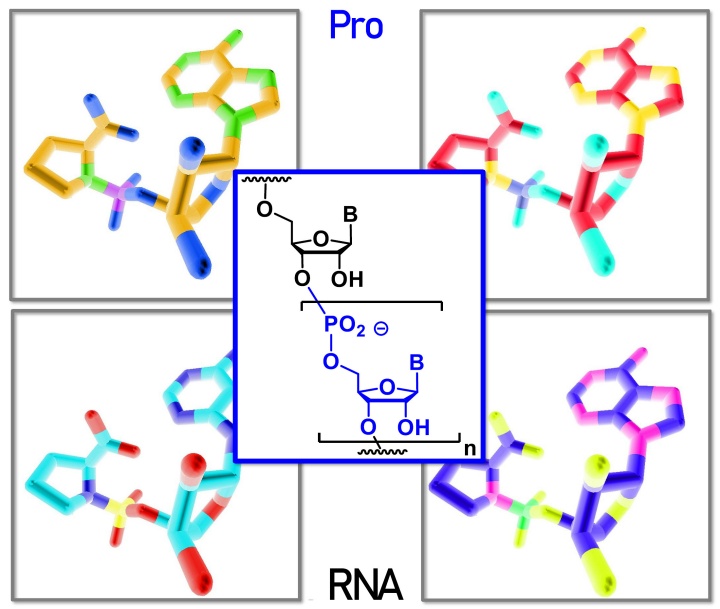
Gabrielle Leveau, Daniel Pfeffer, Bernhard Altaner, Eric Kervio, Franziska Welsch, Ulrich Gerland und Clemens Richert
Dinucleotides as building blocks for the genetic copying of RNA make it possible for the first time to overwrite sequences of up to 12 bases into one copy without enzymes. This is important for the origin of life.
For further information please contact:
Prof. Clemens Richert
Institute of Organic Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
Robert U. StelzerRobert U. Stelzer, Yuji Ikeda*, Prashanth Srinivasan, Tanja S. Lehmann, Blazej Grabowski, und Rainer Niewa
Material for the Li-Sn battery for the highest capacities to date discovered in close cooperation between experimental inorganic chemists and material scientists in theoretical material simulation.
For further information please contact:
Prof. Rainer Niewa
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
Hang Liu, Dr. Hongguang Wang, Dr. Qian Song, Dr. Kathrin Küster, Prof. Ulrich Starke, Dr. Peter A. van Aken und Prof. Elias Klemm
Angew. Chem.Int. Ed.2022, e202117058
For further information please contact:
Prof. Elias Klemm
Institute for Technical Chemistry
University of Stuttgart
Please note: Meetings of the habilitation committee and the grand PhD committee only take place when required.
02. March 2026
Habilitation Committee,
Small PhD Committee
22. April 2026
Grand Faculty Council,
Small PhD Committee
20. May 2026
Grand Faculty Council,
Small PhD Committee
24. June 2026
Grand Faculty Council,
Small PhD Committee
14. October 2026
Grand Faculty Council,
Small PhD Committee,
Grand PhD Committe
11. November 2026
Grand Faculty Council,
Small PhD Committee
16. December 2026
Grand Faculty Council,
Small PhD Committee
27. January 2027
Grand Faculty Council,
Small PhD Committee
https://www.f03.uni-stuttgart.de/fakultaet/#id-dcd6f845-0
There are currently no professorships advertised. Please visit this page regularly for updates on new vacancies.
The Faculty of Chemistry has a glassblowing workshop and a mechanical workshop.
Our workshop commission looks after the interests of the workshops. The head of the commission is Prof. Elias Klemm ITC. Other members are: Dr. Dominik Bloos IPC, Jun.-Prof. Bertold Rasche IAC, Dr. Johannes Ackermann IOC, Prof. Oliver Clemens IMW, Dr. Klaus Dirnberger IPOC and Dipl.-Ing. Ines Lauerwald ITC.
Please note: Our workshops are only responsible for internal university orders.
Order forms for the workshops can be found here (*.docx) and here (*.pdf) (for internal use only).
Office of the Dean

Monika Carey
Secretary

Dorothea Häussermann
Dr.Faculty Manager